ENGINE
General Information
In this section, we will cover both versions of the E
series engine. The DuraForce is a reed valve engine,
and the R tek is piston ported. The design difference
affects the path which the incoming fuel/air charge
takes to get to the firing chamber.
Two-cycle engines have special advantages which
make their use more practical in certain applications.
Two-cycle engines are lightweight with an excellent
power-to-weight ratio and can be operated in any
position, limited only by the carburetor and fuel supply
system. They are also notably easy to maintain and
service because of their uncomplicated design.
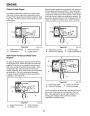
Figure 65
A. Reed Valve Open
3297-021-2
The crankshaft continues its rotation, and the piston
begins its travel toward the spark plug. As it moves,
the piston seals off the transfer port first, then the
exhaust port. When both ports are sealed, the
remaining travel compresses the air/fuel mixture to
prepare it for ignition. The travel of piston towards the
spark plug is called the compression stroke. (See
Figure 65.)
Theory of Operation
Reed Valve Engine
The illustration below (see Figure 64) shows what
happens inside the engine during one full crankshaft
revolution. Fuel intake, fuel ignition, and the exhaust of
burned gases all take place during a single 360-degree
rotation of the crankshaft.
The movement of the piston towards the spark plug
also has an important effect in the crankcase. Once
the transfer port is sealed, a vacuum is created in the
crankcase. This action pulls the reed valve open and
draws in a fresh charge of fuel/air mixture.
Just before the piston reaches top dead center (TDC),
the spark plug fires. When the engine is functioning
properly, the fuel/air mixture ignites, causing a burn
that occurs evenly through the power stroke. The
piston changes direction and begins its travel towards
the crankcase.
NOTE: If the compression ratio is too high, the fuel/air
mixture actually explodes before it is ignited by the
spark plug. This can be heard and is identified as
detonation (also called “knock”).
Figure 64
3297-022-2
A. Reed Valve Closed B. Exhaust Gases
Beginning at a point where the top of the piston is just
below the exhaust port, the piston moves forward
toward the crankcase. As the transfer port is
uncovered, the fuel/air mixture stored in the
pressurized crankcase is forced into the combustion
chamber. (See Figure 65.)
When the piston opens the exhaust port, high-pressure
exhaust gases exit the exhaust port. Further
movement of the piston towards the crankcase
uncovers the transfer port which allows a fresh charge
of air/fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber.
As the exhaust gases continue to exit the exhaust port,
the engine is readied for another cycle.
39
| Categories | Lawn Mower Manual, Lawn-Boy Lawn Mower Manuals, Toro Lawn Mower Manual |
|---|---|
| Download File |
|
| Language | English |
| Product Brand | Toro. Customer Service Representatives are available by phone:
Monday - Friday 7:30 a.m. to 9:00 p.m. (CDT) - Saturday 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. (CDT) - Sunday 10:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. (CDT)
Canada 1-888-225-4886 USA 1-888-384-9939, Lawn Mower |
| Document File Type | |
| Publisher | toro.com |
| Wikipedia's Page | Toro Company |
| Copyright | Attribution Non-commercial |
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)