Preparation for Engine Repair
1. Before cleaning and disassembly, carefully check for
problems that cannot be found after the engine has
been cleaned or disassembled (e.g. oil leaks from
cracked components, gaskets or loose fittings, dam•
aged air cleaner or breather hoses that could cause
cylinder wear, etc.). Make a note of any problems that
you find.
engine oil to disassembled parts, as necessary to pre•
vent rust.
5. Keep the work area clean; dirt causes engine failures.
6. Be very careful when working on fuel system compo•
nents. Cover the work area with clean paper. Store
components of the nozzles or injector pump in clean fuel
oil. Do not allow components to strike each other or
other objects. Wet hands with clean diesel fuel before
handling these parts.
2. Clean or wash the engine exterior thoroughly before
disassembly.
IMPORTANT: Do not spray water on a hot engine.
Injection pump seizure or other failures could
result.
Engine Compression
The time interval to overhaul the engine can most
accurately be determined by regular and systematic
cylinder compression measurement. (See Compres•
sion Test in the Testing section of this chapter.)
3.
require disassembly.
Do not disassemble or remove parts that do not
4.
Disassemble the engine in proper order, arranging
the parts the disassembled parts neatly. Apply clean
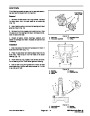
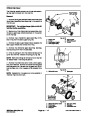
Cylinder and Cylinder Block Overhaul
Before removing any parts, disassembly or overhaul of
the Mitsubishi engine, it is very important to understand
the nature and probable cause of the problem that made
an overhaul necessary.
list can be a result of excessive fuel injection, improper
injection timing, or nozzle and injection pump wear. Poor
starting may be a result of electrical problems. Noises
may be associated with a mechanical part outside the
engine. Excess fuel or oil consumption may be the result
of leaks. (See the Troubleshooting section of this chap•
ter.)
When the engine trouble is caused by worn cylinders,
rings or valves, one or more of the following symptoms
will occur:
Another indicator of the need for an overhaul is oil
consumption. Make sure the engine does not leak oil.
when the oil consumption between the oil change main•
tenance interval is approximately 1-1/2 times normal
(150%), engine overhaul should be considered.
1. Low engine power, and a decrease in compression
pressure.
2. Increased fuel consumption.
3. Increased lubricating oil consumption.
4. Poor engine starting.
With a good knowledge of how the engine operates,
access to maintenance and compression test records,
and information in the Troubleshooting section of this
chapter, unnecessary disassembly and inspection can
be eliminated.
5. Loud noises in the engine.
It is important to find the cause of the engine failure
before beginning repair. Symptoms 2 and 3 in the above
Groundsmaster® 300 Series
Page 4 - 25
Preparation for Engine Repair
| Categories | Lawn Mower Manual, Sprinkler and Irrigation Manuals, Toro Sprinkler and Irrigation Manuals |
|---|---|
| Tags | Toro Groundsmaster 300, Toro Groundsmaster 328 D, Toro Groundsmaster 92801SL |
| Download File |
|
| Document Type | Service Manual |
| Language | English |
| Product Brand | Toro. Customer Service Representatives are available by phone:
Monday - Friday 7:30 a.m. to 9:00 p.m. (CDT) - Saturday 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. (CDT) - Sunday 10:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. (CDT)
Canada 1-888-225-4886 USA 1-888-384-9939, Lawn Mower |
| Document File Type | |
| Publisher | toro.com |
| Wikipedia's Page | Toro Company |
| Copyright | Attribution Non-commercial |
(2 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Lawn and Garden readers have rated Toro 92801SL Rev I Groundsmaster 300 Series Groundsmaster 328 D Service Manual 5.0 out of 5.0 based on 2 product reviews. Need 328D. Manual pdf. Will rate after finding manual
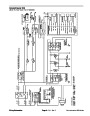
t has been a very reliable machine but getting parts is hard and not cheap to buy , generic parts has been cost effective and reliable , i am unable to get a wiring circut diagram for this unit as most problems are electrical problems